Glossary (64)
Abrasion
The removal of solid material by constant wear – a sign of wear.
Actuator
An actuator is used to move the adjustment spindle for the stroke length adjustment of a motor-driven metering pump, changing the stroke length and the stroke volume. The adjustment position is not automatically fed back to the pump.
Attenuation
Calculation of a medium numeric value over a defined time period which equals a defined number of measured values. The more values are taken to calculate the medium flow value, the more stable the display will be.
Back pressure valve
A back pressure valve has the role of generating a defined stable operating pressure for a metering pump to keep the capacity and thus the metering volume stable. The constant pressure is generated by a spring-loaded mechanism in the valve. A pressure gauge has to be used to adjust the opening pressure in the line.
Biofilm
A biofilm is a film made of different micro-organisms with multiple layers. There are areas of the surface tolerant to oxygen and areas at the base of the biofilm lacking in oxygen.
Calibration
When a metering pump has been installed, the capacity in litres per hour has to be determined under prevailing operating conditions, and particularly at a certain constant operating pressure. This is done using what is known as calibration columns, in which a defined volume is filled and then pumped. The volume pumped per unit of time is then converted into capacity per hour.
Example: A pump has pumped 50 ml in 1 minute at 80% stroke length and 100 strokes per minute. This produces a pump capacity per hour of 50 ml x 60 min = 3000 ml/h = 3 l/h.
CANopen
On the hardware side, all units comply with the harmonised CAN specification 2.0 (ISO99-1, ISO99-2). This includes the CAN protocol (ISO 11898-1) and details on the physical layer in compliance with ISO 11898-2 (high speed CAN up to 1 Mbit/sec) and ISO 11898-3 (low speed CAN up to 125 kBit/sec). The unit complies with the CANopen specification CIA-DS401 that forms the basis of the European standard EN50325-4 and also complies with the controller device profile CiA-404.
Cavitation
The formation of small gas bubbles in a fluid. Cavitation has a detrimental effect on the operation and lifetime of a pump and should therefore be avoided as far as possible.
Chlorine dioxide
Chlorine dioxide is an exceptionally reactive gas, which is not stored due to its instability but rather must only be manufactured to meet requirements at its place of use in special systems.
Chlorine dioxide has a number of advantages over chlorine, which is predominantly used in the disinfection of water. Thus for instance, the disinfection effect does not reduce with increasing pH-value, as is the case with chlorine, rather it increases slightly. Chlorine dioxide remains stable in pipework systems over long periods of time and provides microbiological protection of the water for many hours and up to several days. Ammonia or ammonium, which cause considerable chlorine loss, do not react with chlorine dioxide so that the metered chlorine dioxide remains fully available for disinfection purposes. Chlorophenols, strongly smelling compounds, which result from the chlorination of water etc., are not formed with chlorine dioxide. Trihalogenmethanes (THMs), a substance class, which, like their main representative, chloroform, is suspected of being carcinogens, result from the reaction of chlorine with dissolved matter naturally found in water (humic acids, fulvic acids, etc.). If chlorine dioxide is used as an alternative disinfectant these substances are not produced.
Click wheel
Intuitive control for quick and reliable adjustment of parameters – integrated in the display area. Combined with the clear display and four buttons, it enables easy operation and programming.
The click wheel is a feature of the solenoid driven metering pump gamma/ X.
Combined chlorine
Mono-, di-, trichloroamine. The measuring result of type CLE (free chlorine) is subtracted from the measurement result of type CTE (total chlorine). Reference method: DPD4 minus DPD1
Conductive conductivity
Conductive conductivity sensors measure the electrolytic conductivity indirectly via the charge transfer between two electrodes immersed in the medium to be measured. The sensor types with cell constants k = 0.01 and k = 0.1 cm-1 are especially suitable for the measurement of the lowest electrolytic conductivities of < 1 μS/cm in pure and ultra-pure kinds of water.
The sensor types with cell constants k=1 cm-1 are used in numerous kinds of water without film-forming ingredients up to 20 mS/cm. The cost-effective sensor range LF(T) is used in clear, chemically uncontaminated water.
Corrosion-free
A system is corrosion-free if it experiences minimal or no wear caused by the reaction of the material in contact with chemicals (e.g. chlorine).
Detachable operating unit (HMI)
The operating unit (Human Machine Interface) can be attached directly to the metering pump or mounted on the wall alongside the pump. This provides the operator with a range of options for the integration of a metering system in the overall system that it is readily accessible and easy to use. Moreover the removable operating unit offers additional protection against unauthorised operation of the metering pump or against modification of the pump settings. The operating unit can, for example, be completely removed for project applications.
Individual functions of the metering pump can be easily selected and adjusted with five program keys. An illuminated LCD display provides information about the relevant operating status. LEDs on the operating unit and the control unit indicate the active pump functions or the pump status.
Diaphragm position control
The patented diaphragm position control reliably protects against damage in the event of a blockage on the suction or discharge side. A sensor detects the diaphragm deflection and controls the solenoid coil according to the required stroke. The diaphragm position control is a feature of hydraulic diaphragm metering pumps of the Orlita® Evolution product range.
Diaphragm rupture warning system
In the event of a diaphragm rupture, the feed chemical enters the layer between the diaphragm coatings and thereby triggers a mechanical display and/or alarm via the sensors. This concept ensures reliable metering, even under critical operating conditions.
Dissolved oxygen
The measured variable "Dissolved oxygen" indicates the volume of gaseous oxygen physically dissolved in the aqueous phase in mg/l (ppm).
"Dissolved oxygen" is therefore an important parameter for assessing the quality of surface water and water that has to be treated for the breeding of livestock with the addition of oxygen. Dissolved oxygen is also used for controlling processes in clarification plants and waterworks.
Dosing head
The dosing head is where the actual dosing process takes place. The feed chemical flows in and when it has reached a sufficient pressure it flows out through the discharge valve. The dosing head is located in the liquid end.
Easy Drive
Precise software-based speed control of recirculation to reduce energy costs and pump wear – integrated in the pool control software EcoPad. Based on the data of the multi-parameter controller DULCOMARIN® II, measured with DULCOTEST® sensors. The EcoPad software optimises the pump speed, temperature, backwashing and the consumption of additives for disinfection and pH balancing.
ECA system
Electrolysis system for the production of electrochemically activated water (ECA water). The system produces the effective, economical and environmentally compatible cleaning and disinfection agent directly on site. ECA systems of the DULCO®Lyse series generate ECA water with an exceptionally low chloride content.
ECA water
Generally referred to as ECA water, hypochlorous acid (HCIO) is increasingly used as a disinfectant in the food and beverage industry. It is a colourless, only weakly dissociating acid with a chlorinated lime smell. It has a bleaching and oxidising effect and is very good for disinfection.
Eccentricity
Deviation from a circle to an elliptical shape. Changes in eccentricity occur for example when the pump drive is idle.
Eco!Mode
Eco!Mode permits lowering of the circulation capacity when the DIN hygiene parameters pH, ORP, free chlorine and combined chlorine are within the permitted limits.
A circulating pump with frequency converter with analogue input is needed for this.
The reduction can be activated via a remote control, dependent on the DIN hygiene parameters being observed, the time and appropriate activation. A combination of criteria is also possible. If the DIN hygiene parameters are no longer adhered to, then the circulation capacity is again raised to the nominal power.
Lowering pump capacity saves energy and, in so doing, reduces CO2 emissions.
In addition, upon reaching an adjustable redox potential, e.g. 780 mV, which signals effective disinfection of the water, chlorine metering is reduced either gradually or in one step. If the DIN hygiene parameters are no longer adhered to, then the chlorine metering is again raised to the normal setpoint.
Electrolysis
Chlorine and sodium hydroxide are produced in-situ in electrolysis by passing an electric current through salt water.
In open or tubular cell electrolysis, the electrochemical reaction takes place in a flow chamber, so that the freshly produced active chlorine immediately reacts with the sodium hydroxide to form sodium hypochlorite. A saturated brine is used as a salt solution, which is produced in a separate salt dissolving tank from salt of a defined quality.
In diaphragm electrolysis, the electrochemical reaction takes place in two electrode chambers separated by a diaphragm, so that the formation of the freshly produced active chlorine and sodium hydroxide is physically separated.
Explosion protection
Approved for use in areas at risk of explosion in accordance with ATEX. ATEX: The current EC Directive 94/9/EC (ATEX), which governs the metering of liquid media in areas with an explosive gas atmosphere and mines with a risk of firedamp. All metering pumps in the ProMinent EXtronic® product range come with explosion protection.
Free (effective) chlorine
Recommended sensors for Cl2, HOCl (hypochlorous acid), OCl- (hypochlorite): Types CLE, CLO, CLB and CBR. Reference method: DPD1.
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is used as corrosion inhibitor in water and steam systems. Because of the carcinogenic effect of hydrazine, special preparation and dosing units are required.
Hydrogen peroxide
Due to its complete biodegradability, hydrogen peroxide is a disinfectant and oxidising agent frequently used in water treatment and production:
chemical bleach in the wood, paper, textile and mineral compounds industries,
- organic synthesis in the chemical, pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries,
- oxidation of potable water, landfill seepage water, contaminated ground water,
- disinfection of cooling, process and production water in the pharmaceutical, food and beverage industries as well as in swimming pools,
- deodorisation (gas scrubbers) in municipal and industrial clarification plants,
- dechlorination in chemical processes.
Measured variables
The physical variables to be determined by measuring.
Measuring range
Defined measurable range within which the errors in a measured variable remain within defined limits.
Membrane filtration
In water treatment, membrane filtration is the process for removing particles and salts in the water ensuring the lowest operating costs.
Membrane filtration is a physical process to separate substances with the help of semi-permeable membranes. There are four types of processes, depending on the size of the particles/molecules to be removed:
- Microfiltration
- Ultrafiltration
- Nanofiltration
- Reverse osmosis
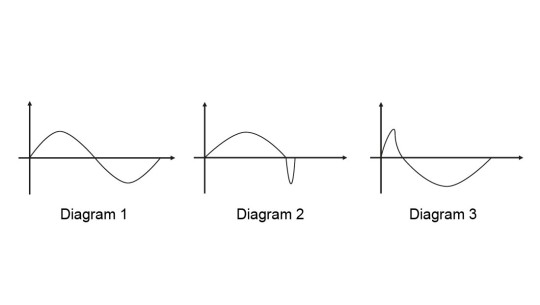
Metering profiles
Metering profiles guarantee optimum metering results by adapting the metering behaviour of the metering pump to the application or chemical used.
The stroke motion of the displacement body is continually recorded and regulated so that the stroke is made in line with the desired metering profile. The pump can be operated in normal mode (Diagram 1), with optimised discharge stroke (Diagram 2) or with optimised suction stroke (Diagram 3). Three typical metering profiles are shown schematically with the behaviour over time.
In normal operating mode, the time behaviour for the suction stroke and the discharge stroke is similar (Diagram 1). In the mode with optimised discharge stroke (Diagram 2), the discharge stroke is lengthened while the suction stroke is made as quickly as possible. This set-up is suited to applications which require optimum mixing and as continuous a mixing of chemicals as possible, for example.
In the mode with the optimised suction stroke (diagram 3), the suction stroke is carried out as slowly as possible, permitting precise and trouble-free metering of viscous and gaseous media. Select this setting to minimise the NPSH value as well.
Microfiltration
A process that occurs in membrane filtration. In microfiltration, particles smaller than 0.1 µm (or smaller than 500,000 Da) are filtered out, such as suspended particles, colloidal turbidities and oil emulsions. Smaller particles can be removed with ultrafiltration and nanofiltration.
Mounting plate
A handy module for fast and straightforward installation: the pump is directly attached to the mounting plate supplied and clips perfectly into place. Conveniently insert the cables into the front connectors – and you're done! Horizontal or vertical: the mounting plate itself can either be bolted to a smooth, load-bearing horizontal or vertical base. It can also be mounted on a wall bracket if required.
Currently available for the solenoid driven metering pump gamma/ X.
Multifunction valve
The multifunctional valve builds up a defined back pressure when metering against a free outlet. This function can be stopped manually. Functions:
- Generation of a defined back pressure when metering against a free outlet.
- Prevents through-suction from the storage tank in the event of negative pressure at the point of injection.
Multi-layer diaphragm
The multi-layer diaphragm (a minimum of two diaphragm layers on top of each other) prevents the escape of the feed chemical in the event of a fault. In addition, the diaphragms also feature a diaphragm rupture warning system. As wear parts, diaphragms have to be regularly checked and replaced if necessary.
Nanofiltration
Nanofiltration is based on the same principle as reverse osmosis. The difference: The separation limit is slightly lower. Admittedly this type of membrane filtration retains ions dissolved in water, but to a significantly lesser extent than with reverse osmosis. Ultimately that saves operating costs.
Typical salt retention rates are around 80 – 90%. Multi-value ions (e.g. Ca and Mg) are retained better than single-value ions (e.g. Na, K) so that nanofiltration systems are often also used as an alternative to traditional water softening.
NPSH value
NPSH is an initialism for Net Positive Suction Head. In any cross-section of a generic hydraulic circuit, the NPSH parameter shows the difference between the actual pressure of a liquid in a pipeline and the liquid's vapor pressure at a given temperature.
NPSH is an important parameter to take into account when designing a circuit: whenever the liquid pressure drops below the vapor pressure, liquid boiling occurs, and the final effect will be cavitation: vapor bubbles may reduce or stop the liquid flow, as well as damage the system.
More at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NPSH
OPC
OPC stands for Openness, Productivity, Collaboration (formerly OLE for Process Control) and is used to describe a uniform software interface independent of specific manufacturers. OPC Data Access (OPC DA) is based on Windows COM (Component Object Model) and DCOM (Distributed Component Object Model) technology. OPC XML, in contrast, is based on the internet standards XML, SOAP and HTTP.
OPC is used wherever sensors, controllers and controls supplied by different manufacturers are used to create a common, flexible network.
OptoDrive®
The controlled solenoid drive OptoDrive® permits the individual and precise timed adjustment of the metering flow – from a slow discharge stroke to fast cyclical bottling processes. Incomplete filling of the liquid end, cavitation and back pressure fluctuations in the metering line are avoided. OptoDrive® guarantees dosing precision that otherwise would only be achievable with complex control circuits.
OptoDrive® with OptoGuard® are features of solenoid metering pumps of the delta® product range.
OptoGuard®
The point of injection monitoring function OptoGuard® detects and reports faulty hydraulic conditions, such as overpressure, ruptured metering line, blocked points of injection and trapped air or gas bubbles in the dosing head. Incorrect dosing is thereby avoided. The messages appear in the display and – depending on the individual pre-selection – are sent by fault indicating relay to the process control system, where an automatic metering stop can be triggered.
OptoDrive® with OptoGuard® are features of solenoid metering pumps of the delta® product range.
Overload cut-off
The pump is switched off electronically when it exceeds a defined tolerance range. The overload switch protects the pump, guaranteeing maximum safety for your investment.
Overload switch-off
Prevents overloading of the pump by automatically switching it off.
Peracetic acid
Peracetic acid is particularly used in the food and beverage industry, but also for disinfection in the cosmetics, pharmaceutical and medical sectors. The continuous measurement and control of peracetic acid is therefore required when there are high demands in terms of disinfection and quality assurance.
Peristaltic pump
This is how they work: The feed chemical is pumped by the rotor clamping the hose in the direction of flow. No valves are needed. Abrasive, viscous and gaseous media can thereby be gently conveyed.
Permeate output
Value indicating what amount of a liquid (e.g. water) can permeate a material (e.g. a diaphragm used for filtering) in a specified period of time.
Phosphate
Ortho and polyphosphate revent limescale and corrosion in hard water up to max. 20 CH (carbonate hardness). Hard water salts, such as calcium and magnesium ions, responsible for limescale are thereby stabilised, i.e. these ions remain dissolved in the water and do not form limescale on the pipe walls. Growth on the pipes is thus prevented and there are no deposits of limescale on heating coils, dramatically reducing their efficiency. A thin, solid protective layer is formed.
pH value
The pH value is a measure of the acidic or basic character of an aqueous solution.
Neutral fluids, such as water, have a pH of about seven. The lower the value, the more acidic is the liquid. The liquid becomes more alkaline as the pH increases.
PID controller
Controls processes automatically to ensure that the specified values (e.g. pH: acid or alkaline) are maintained even in the event of interfering influences. As a universal controller, the PID (Proportional–Integral–Differential) controller delivers reliable results. It is used in ProMinent measuring and control technology as a monodirectional and bidirectional controller.
The PID controller is a standard component of the DULCOMETER® control devices DULCOMARIN® II, diaLog DACa, Compact, D1Cb and D1Cc.
Polyelectrolyte
Polyelectrolytes are used as flocculants in all applications where colloidal solids have to be economically separated from liquids.
ProMinent value added service
Knowledgeable advice and first-class support: phone support with reliable availability, advice on technical applications, individual configuration of the pump and expert on-site customer service.
This comprehensive service is available for the hydraulic diaphragm metering pump Orlita® Evolution and the solenoid driven metering pump gamma/ X.
Pulsation damper
Damps the pulsation (dynamic pressure changes in the fluid) and reduces the flow resistance in long metering lines. Damping is achieved by a gas cushion in the pulsation damper, which is compressed on every compression stroke. The pulsation damper is installed in the pipe or diagonally across with a set of blanking plugs. Important: It should always be protected by a relief valve.
Reproducibility
The degree of consistency between independently determined measured values under defined conditions.
Residual
Describes the ability of a substance to have a long-term effect and maintain this under certain conditions.
Reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis is a sub-sector within membrane filtration. It is the process with the highest separation limit and represents the reversal of the natural process of osmosis. It is therefore used as a method for desalinating aqueous solutions. With suitable high-performance diaphragms, it is possible today to remove over 99% of all salts from an aqueous solution.
Servo motor
A servo motor is used to automatically adjust the stroke length of a motor-driven metering pump as a function of a 0/4-20 mA signal. 0/4 mA corresponds to 0 % stroke length. 20 mA correspond to 100 % stroke length. The stroke position response signal is transmitted to the pump via a variable signal.
Silicate
Silicate is used as a corrosion inhibitor to prevent rust formation ("brownish water" in galvanised piping systems) and "pitting" (needle-like holes in the pipework). Applications include soft, corrosive types of water with a high percentage of aggressive carbonic acid. The silicate is used to raise the pH value closer to a lime-carbonic acid equilibrium. Hydrolysis produces a silica gel that forms a thin protective layer in the pipework and fittings and thus prevents corrosion.
Total available chlorine
Chlorine bound to (iso)cyanic acid/isocyanurate and the free (effective) chlorine resulting from it. Recommended sensor: Type CGE, reference method DPD1.
Total chlorine
Total of free and combined chlorine. Recommended sensor: Type CTE, reference method DPD4.
Ultrafiltration
Ultrafiltration is a membrane process which is increasingly used in water treatment to separate undesired water components. Parasites, bacteria, viruses and high-molecular organic substances as well as other particles are retained.
The applications of ultrafiltration are widespread and may include different types of water.
Typical applications include drinking water, river water, process water, swimming pool water, salt water and waste water.
UV disinfection
With UV disinfection, the water to be disinfected is irradiated with ultraviolet light, which involves a purely physical, chemical-free process for water disinfection.
UV-C radiation in particular, with a wavelength ranging from 240 to 280 nm, attacks the vital DNA of the bacteria directly. The radiation initiates a photochemical reaction and destroys the genetic information contained in the DNA. The germ loses its reproduction capability and is destroyed. Even parasites, like Cryptosporidia or Giarda, which are extremely resistant to chemical disinfectants, are efficiently reduced.
Vacuum process
Process which allows high-purity substances (e.g. active chlorine) to be generated through the absence of oxygen and other gases. This process is used in the electrolysis system CHLORINSITU®.
Web server
A web server is a software application executed by the DULCOMARIN® II.
The web server delivers web pages with information about measurements, control, sensor calibration and control configuration to a PC with a web browser (e.g. Microsoft® Internet Explorer).
The web server enables simple and straightforward visualisation of the DULCOMARIN® II, without special visualisation software being required on the PC. The web server is independent of the PC's operating system.
Wiper system
Efficiently removes deposits on the lamp protection tubes without chemicals or interruptions to operation – even at full operating pressure. The position of the wiper is checked multiple times during the wiping process. The continuous exchange of data between the wiper motor and controller guarantees reliable cleaning. A feature of the comfort controller UVCb for certain UV systems from the Dulcodes range.
Contact us

Product Overview 2024
Dosing technology, measurement, control and sensor technology, water treatment and water disinfection as well as digital solutions

ProMinent Product Catalogue 2024 - Volume 1: Metering Technology
Low-pressure metering pumps
Peristaltic metering pumps
Motor-driven metering pumps
Transfer and peristaltic pumps
Metering systems
Process metering pumps

ProMinent Product Catalogue 2024 - Volume 2: Measuring, Control and Sensor Technology
Sensors
Controllers
Measuring and control points
Treatment of swimming pool water

ProMinent Product Catalogue 2024 - Volume 3: Water Treatment and Water Disinfection
UV systems
Ozone systems
Chlorine dioxide
Electrolysis systems
Metering systems ULTROMAT and DULCODOS
Storage tanks
Diaphragm systems